Here is the teardown of the Xiaomi SU7’s headlight driver board . We found its driver module is a showcase of automotive-grade electronics. The board leverages a core automotive MCU from Infineon, dual CAN transceivers from NXP for reliable communication, and dedicated LED drivers from Texas Instruments for precise lighting control.
BOM Analysis
| Manufacturer | Part Number | Description |
| Infineon | CYT2B75CADQ0AZEGS | 32-bit Arm Cortex-M4 based MCU |
| NXP | TJA1042 | CAN Transceiver |
| NXP | TJA1043 | CAN FD Transceiver |
| MPS | MP2019 | Adjustable Output Linear Regulator |
| onsemi | NCV70517 | Microstepping Motor Driver |
| ROHM | BD42530 | Low Quiescent Current Voltage Follower |
| Diodes | DMPH4015SPSQ | P-Channel MOSFET |
| Diodes | DMTH8008LPSQ | N-Channel MOSFET |
| GOOD-ARK | AMBRP10H100 | Schottky Barrier Rectifier |
| Diodes | DMTH8008LPSQ | N-Channel MOSFET |
| GOOD-ARK | AMBRP10H100 | Schottky Barrier Rectifier |
Teardown Reflection
To be honest, when I first saw the rear shell of the Xiaomi SU7 headlight driver module, I almost thought I had bought a “counterfeit” part. After all, the headlight driver module I disassembled from the AITO M7 earlier was fully metal. Later, I found that most modules on the market look like this, so I felt relieved. However, during the actual teardown, I discovered that the SU7 headlight driver module was not easy to open because a lot of adhesive was used at the junction between the bottom shell and the metal front cover. In the end, I had to completely break the rear cover to remove the driver board.
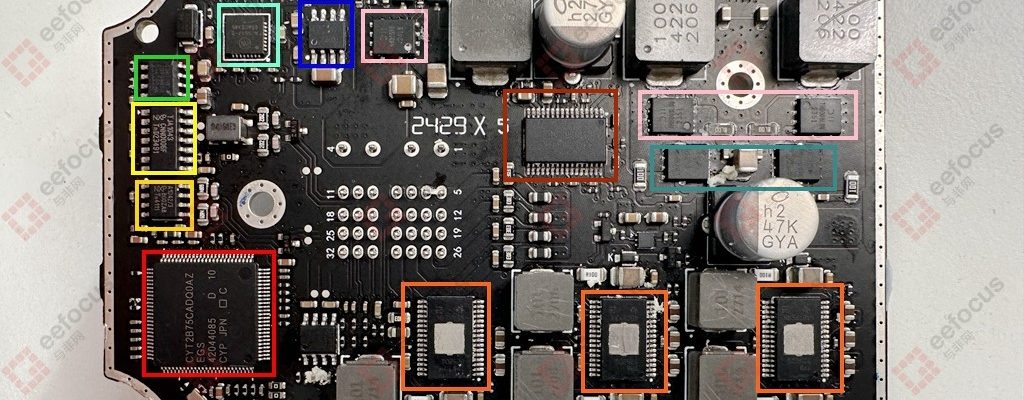
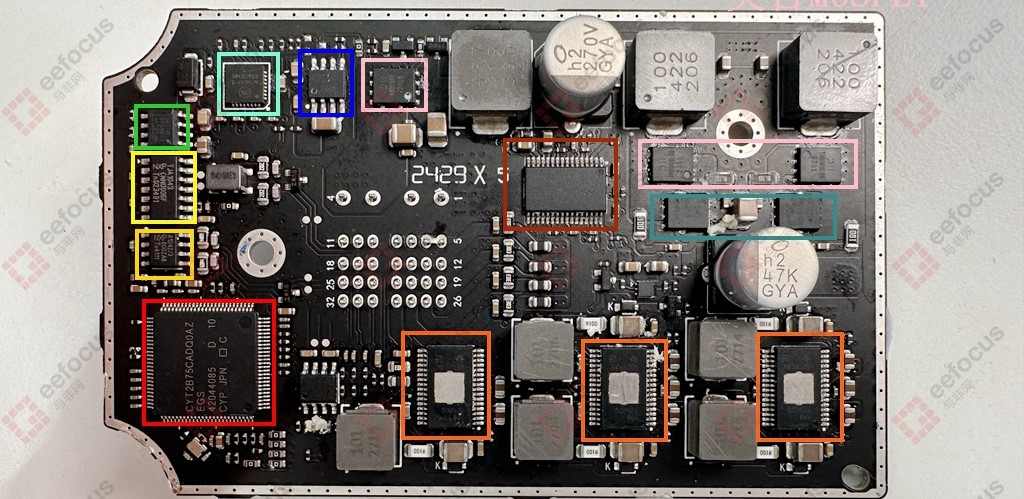
At first glance at this black PCB and its component layout, it looks pleasing to the eye. Moreover, the back of the PCB has no components, only an external interface, so the focus is on the side with the components.
- onsemi Micro Stepping Motor Driver
- TI Dual-Channel Constant Voltage LED Driver
- Suzhou Good-Ark Schottky Barrier Rectifier
- MPS Linear Regulator
- ROHM Voltage Follower
- Diodes MOSFET
- Infineon Microcontroller
- TI Dual Synchronous Buck LED Driver
- NXP CAN Transceiver TJA1042
- NXP CAN Transceiver TJA1043
The core controller is an automotive-grade MCU from Infineon (CYT2B75CADQ0AZEGS), based on the Arm Cortex-M4 core. It handles the main lighting logic operations, provides PWM waveform generation, fault diagnostics, and runs the communication protocol stack.
There are two CAN bus controllers, both from NXP. The use of two chips suggests a redundant communication design. The SOP8 package model is TJA1042, a basic CAN bus transceiver responsible for body network communication. The SOP14 package model is TJA1043, which differs from TJA1042 by supporting CAN FD with a transmission rate of up to 5 Mbps. This is likely designed for high-bandwidth lighting commands to meet dynamic beam pattern data transmission needs.
MPS provides the linear regulator (MP2019), which fully covers the transient voltage fluctuations of a 12V vehicle input and features ultra-low quiescent current to reduce standby power consumption.
onsemi supplies the microstepping motor driver (NCV70517), a function typically found only in mid-to-high-end traditional fuel vehicles. It drives headlight adjustment to enable AFS adaptive steering lighting.
ROHM offers the voltage follower (BD42530), likely used for dynamic voltage tracking of the lamp assembly. Its ±10 mV offset voltage ensures beam control accuracy and solves brightness fluctuations caused by cable voltage drops.
The main LED lighting system is implemented using chips from Texas Instruments. From the circuit design, it is divided into a main LED driver and an auxiliary LED driver. The main LED driver uses TI’s dual-channel constant-voltage LED driver (TPS92682Q), which supports PWM dimming and drives high-current LED strings via external MOSFETs. These MOSFETs include two from Diodes Incorporated (DMPH4015SPSQ) and two Schottky diodes from GOOD-ARK (AMBRP10H100). The auxiliary LED driver uses three TI dual synchronous buck LED drivers (TPS92520Q), each with a 1.6A output capability, likely for auxiliary light sources such as daytime running lights.
Other components on the PCB include another P-channel MOSFET from Diodes Incorporated (DMPH4015SPSQ) and a SOP8-packaged chip marked “2LZ15,” for which no manufacturer or model information was found. If anyone knows, please leave a comment—much appreciated!